本篇介绍了如何使用ESP8266,通过WIFI连网获取网络天气和网络时间,然后借助U8g2库,在OLED上显示当前时间和天气信息。
1 HTTP获取网络天气
连网获取网络天气,一般需要通过http的方式,从天气信息提供商的网络地址获取天气信息。
1.1 注册开发者key
这里以心知天气为例,需要先注册一个开发者账号,然后获取自己的私钥,也就是等下要用到的key。
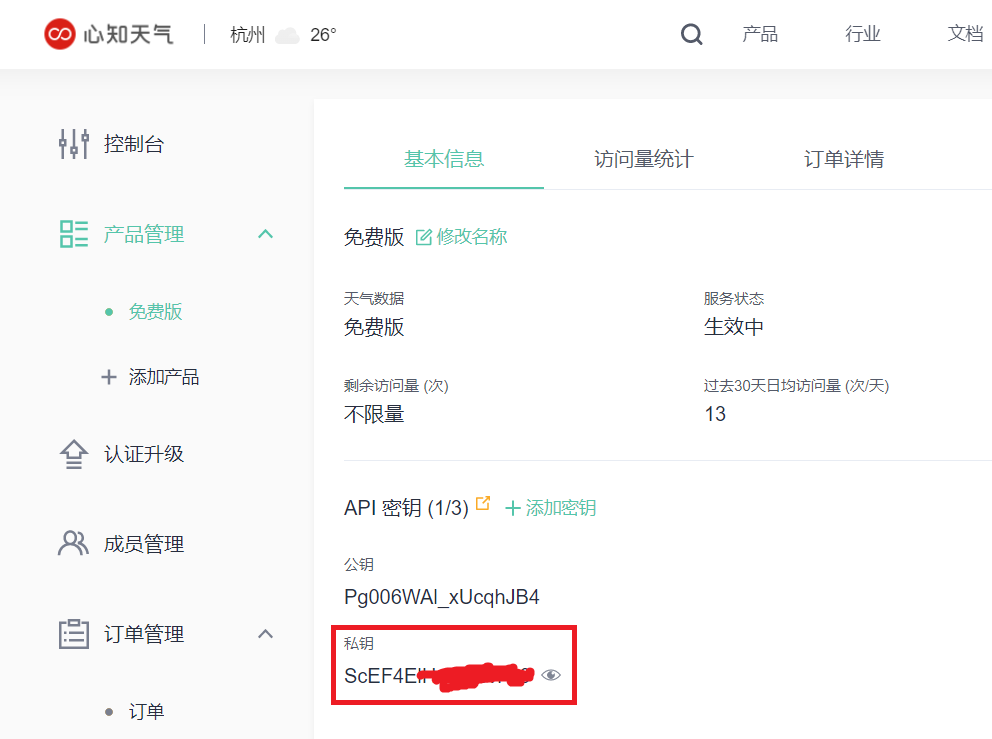
然后可以先在浏览器中输入如下链接,注意要将自己的key替换进去,然后就可以测试一下天气信息的获取情况。
https://api.seniverse.com/v3/weather/now.json?key=替换为你的私钥&location=HangZhou&language=en&unit=c
如下即为获取的天气信息,是json格式的:
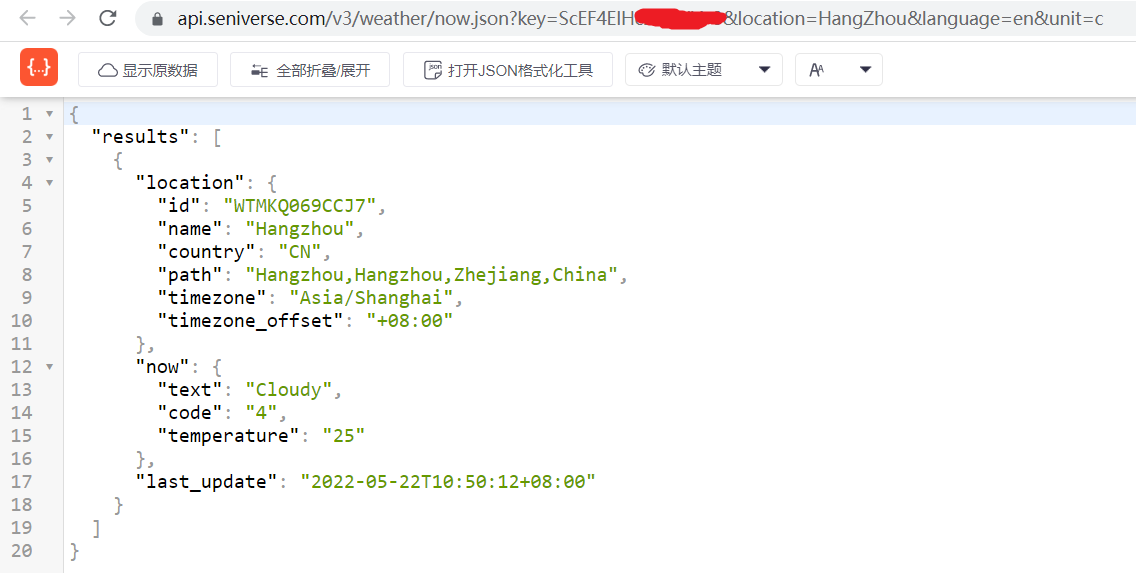
1.2 http请求基本原理
上面先通过浏览器的方式获取到了天气信息,而ESP8266没有浏览器功能,需要编写代码实现http数据请求。
在编写代码之前,需要先了解一下基础的http请求原理。
url全称是资源描述符,一个url地址,用于描述一个网络上的资源,而http中的get、post、put、delete就对于着这个资源的查、改、增、删4个操作,get一般用于获取/查询资源信息。
url的格式:
【协议】://【主机名(或者叫域名)】【:端口号(可选)】/【文件路径】/【文件名】
例如:https://api.seniverse.com/v3/weather/now.json?key=替换为你的私钥&location=HangZhou&language=en&unit=c
- 协议:https
- 域名:api.seniverse.com
客户端发送一个HTTP请求到服务器的请求消息包括以下格式:请求行(request line)、请求头部(header)、空行和请求数据四个部分组成,下图给出了请求报文的一般格式。
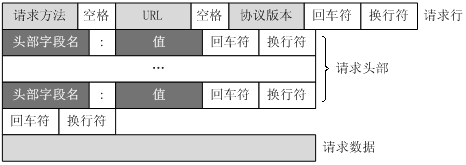
服务器HTTP响应也由四个部分组成,分别是:状态行、消息报头、空行和响应正文。

根据http协议,可以编写ESP8266进行http请求的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| const char* host = "api.seniverse.com";
const int httpPort = 80;
String reqUserKey = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
String reqLocation = "HangZhou";
String reqUnit = "c";
String reqRes = "/v3/weather/now.json?key=" + reqUserKey +
+ "&location=" + reqLocation +
"&language=en&unit=" +reqUnit;
String httpRequest = String("GET ") + reqRes + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" +
"Host: " + host + "\r\n" +
"Connection: close\r\n\r\n";
WiFiClient client;
if (client.connect(host, 80))
{
client.print(httpRequest);
Serial.println("Sending request: ");
Serial.println(httpRequest);
String status_response = client.readStringUntil('\n');
Serial.print("status_response: ");
Serial.println(status_response);
if (client.find("\r\n\r\n"))
{
Serial.println("Found Header End. Start Parsing.");
}
parseInfo(client);
}
|
1.3 json数据解析
http请求获取到的天气数据是json格式的(关于json的介绍可参考:),需要对数据进行解析,获取到具体的天气和温度等数据。
可以将获取的json原始数据打印出来,方便确认程序是否获取到的天气数据。
具体代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| void parseInfo(WiFiClient client)
{
const size_t capacity = JSON_ARRAY_SIZE(1) + JSON_OBJECT_SIZE(1) + 2 * JSON_OBJECT_SIZE(3) + JSON_OBJECT_SIZE(6) + 230;
DynamicJsonDocument doc(capacity);
deserializeJson(doc, client);
Serial.println(doc.as<String>());
JsonObject result0 = doc["results"][0];
JsonObject result0_now = result0["now"];
g_strWeather = result0_now["text"].as<String>();
g_iCode = result0_now["code"].as<int>();
g_iTemperature = result0_now["temperature"].as<int>();
g_strUpdateTime = result0["last_update"].as<String>();
Serial.println(F("======Weahter Now======="));
Serial.print(F("Weather Now: "));
Serial.print(g_strWeather);
Serial.print(F(" -> "));
Serial.println(g_iCode);
Serial.print(F("Temperature: "));
Serial.println(g_iTemperature);
Serial.print(F("Last Update: "));
Serial.println(g_strUpdateTime);
Serial.println(F("========================"));
}
|
原始json格式的天气数据和解析后的天气和温度数据如下:
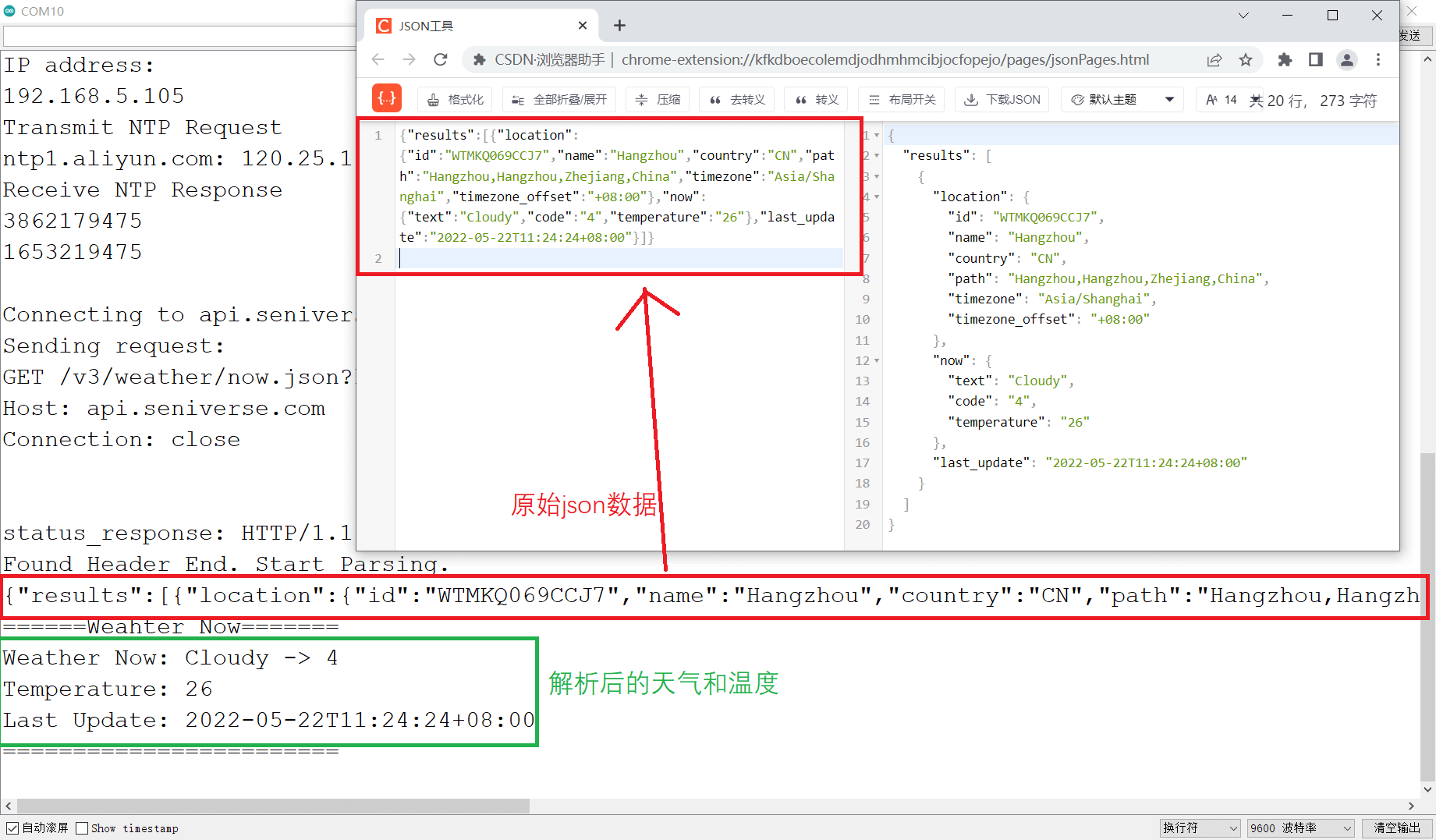
天气现象代码对照表
解析到的天气数据,除了英文形式的天气信息(text),还有一个对应的天气码(code),如上图的Cloudy对应的天气码是4。通过天气码,也可以转换为天气。天气码的对照表可参考心知天气文档:https://docs.seniverse.com/api/start/code.html

简化起见,这里只使用常用的4种天气。
| 代码 |
中文 |
英文 |
| 0 |
晴(国内城市白天晴) |
Sunny |
| 4 |
多云 |
Cloudy |
| 9 |
阴 |
Overcast |
| 13 |
小雨 |
Light Rain0 |
2 NTP网络时间
NTP(Network Time Protocol) 是网络时间协议,它是用来同步网络中各个计算机时间的协议。
ESP8266可以连网,那就也可以通过获取网络时间来得到当前的时间:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| time_t getNtpTime()
{
IPAddress ntpServerIP;
while(Udp.parsePacket() > 0);
Serial.println("Transmit NTP Request");
WiFi.hostByName(ntpServerName, ntpServerIP);
Serial.print(ntpServerName);
Serial.print(": ");
Serial.println(ntpServerIP);
sendNTPpacket(ntpServerIP);
uint32_t beginWait = millis();
while (millis() - beginWait < 1500)
{
int size = Udp.parsePacket();
if (size >= NTP_PACKET_SIZE)
{
Serial.println("Receive NTP Response");
isNTPConnected = true;
Udp.read(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
unsigned long secsSince1900;
secsSince1900 = (unsigned long)packetBuffer[40] << 24;
secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[41] << 16;
secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[42] << 8;
secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[43];
Serial.println(secsSince1900);
Serial.println(secsSince1900 - 2208988800UL + timeZone * SECS_PER_HOUR);
return secsSince1900 - 2208988800UL + timeZone * SECS_PER_HOUR;
}
}
Serial.println("No NTP Response :-(");
isNTPConnected = false;
return 0;
}
|
3 OLED显示页面设计
获取到天气信息和时间后,需要将这些信息显示出来。
这里使用0.96寸OLED显示屏来显示,借助U8g2库,显示文字与天气图标(U8g2库的使用,可参考:)。
具体的显示代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| void testShowTimeAndWeather(rtc_time_t &now_time, weather_info_t &weather_info)
{
u8g2.clearBuffer();
int tm_year = now_time.tm_year;
int tm_month = now_time.tm_mon;
int tm_day = now_time.tm_mday;
int tm_hour = now_time.tm_hour;
int tm_minute = now_time.tm_min;
int tm_sec = now_time.tm_sec;
int tm_week = now_time.tm_week;
char str_big_time[] = "";
my_strcat(str_big_time, tm_hour);
strcat(str_big_time,":");
my_strcat(str_big_time, tm_minute);
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_logisoso24_tf);
u8g2.drawStr(0, 30, str_big_time);
char str_small_sec[] = "";
my_strcat(str_small_sec, tm_sec);
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_wqy14_t_gb2312);
u8g2.drawStr(73, 30, str_small_sec);
char str_date[] = "";
char str_temp[6];
itoa(tm_year,str_temp,10);
strcat(str_date,str_temp);
strcat(str_date,"-");
my_strcat(str_date, tm_month);
strcat(str_date,"-");
my_strcat(str_date, tm_day);
u8g2.drawStr(0, 47, str_date);
u8g2.setCursor(0, 63);
u8g2.print("星期");
switch (tm_week)
{
case 1: u8g2.print("日"); break;
case 2: u8g2.print("一"); break;
case 3: u8g2.print("二"); break;
case 4: u8g2.print("三"); break;
case 5: u8g2.print("四"); break;
case 6: u8g2.print("五"); break;
case 7: u8g2.print("六"); break;
default: break;
}
u8g2.setCursor(60, 63);
u8g2.print("杭州");
u8g2.drawLine(90, 0, 90, 63);
if (weather_info.iconIdx<0 || weather_info.iconIdx>3)
{
Serial.print("no icon for weather: ");
Serial.println(weather_info.weather);
}
else
{
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_open_iconic_weather_4x_t );
u8g2.drawStr(96, 34, icon_index[weather_info.iconIdx]);
}
char temperature_tmp[25];
itoa(weather_info.temp, temperature_tmp, 10);
strcat(temperature_tmp,"℃");
u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_wqy16_t_gb2312);
u8g2.setCursor(96, 55);
u8g2.print(temperature_tmp);
u8g2.sendBuffer();
}
|
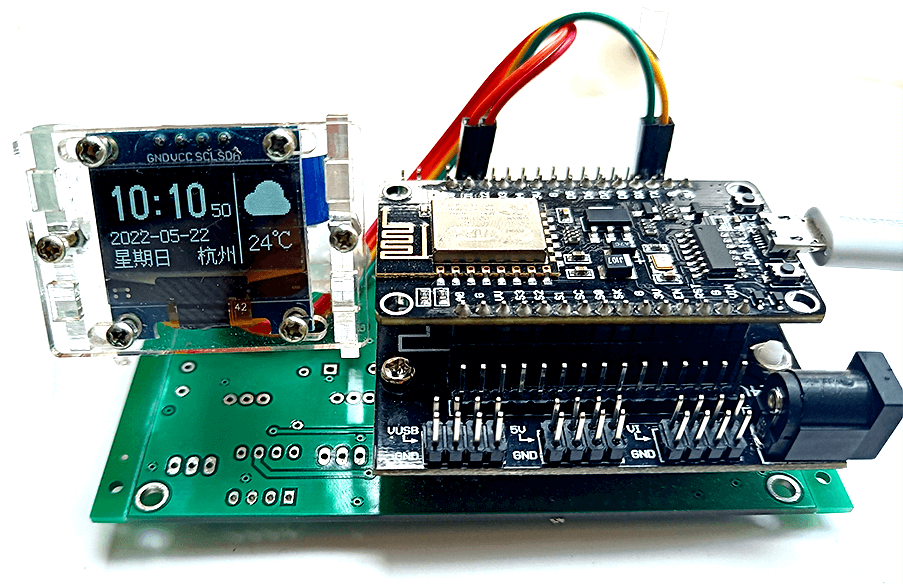
4 最终效果
5 总结
本篇介绍了http获取网络天气的基本原理,并通过实践,使用ESP8266连网获取网络天气和网络时间,借助U8g2库,在OLED上显示当前时间和天气信息。
















